[자료구조/ 알고리즘] Queue
by 꽈배기
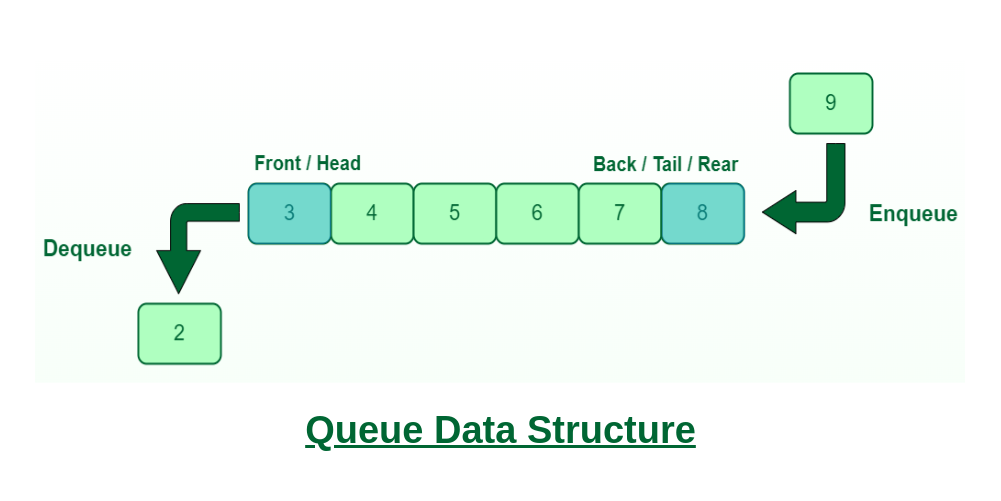
Queue
큐는 FIFO의 성격을 가지는 자료구조이다.
FIFO(가장 먼저 들어온 것이 가장 먼저 나간다.)
Queue의 멤버 함수로는..
- push
- pop
- front 이며 각각 n(1)의 상수 시간을 가진다.
내부 데이터를 살펴보면
class Queue
{
private:
int front;
int rear;
int cs;
int ms;
int * arr;
};
queue 인덱싱 front, rear 그리고 사이즈 currentSize, maxSize 내부의 데이터를 저장할 배열이 멤버로 존재한다.
Queue using Circular Array
// circular queue
template<typename T>
class myQueue
{
private:
int front;
int rear;
int cs;
int ms;
T * arr;
public:
myQueue(int MAX_SIZE = 5)
{
ms = MAX_SIZE;
arr = new T[ms];
cs = 0;
front = 0;
rear = ms -1;
}
bool full()
return cs == ms;
bool empty()
return cs == 0;
void pop()
{
if(!empty())
{
front = (front+1) % ms;
cs--;
}
}
void push(T d)
{
if(!full())
{
rear = (rear+1) % ms;
arr[rear] = d;
cs++;
}
}
T Front()
return arr[front];
};
큐 멤버에는 배열이 존재하는데, 이에 순환을 넣은 큐를 원형큐라고 한다.
원형큐는 삽입과 삭제에 따른 공간 변화를 front, rear, maxSize, currentSize로 판단하여 순환을 돈다.
원형 큐
void pop()
{
if(!empty())
{
front = (front+1) % ms;
cs--;
}
}
void push(T d)
{
if(!full())
{
rear = (rear+1) % ms;
arr[rear] = d;
cs++;
}
}
위의 멤버 함수 pop, push를 보면 각 front와 push의 연산에 해당 부분이 들어간다
front = (front+1) % ms;
rear = (rear+1) % ms;
이는 front와 rear가 maxSize에 다다르면 첫번째 인덱스로 보내주는 역할을 한다. 이로써, 처음과 끝이 이어진 원형큐가 되는것이다.
Stack using 2 Queues
Queue 두개를 이용해 스택처럼 사용하는 방법이다. queue 두개를 스위칭 해가며 마지막 인자에 pop 또는 top을 해주면 된다고 한다.
자료구조 관점에서 생각해보자.
stack의 구성요소는…
- pop
- push
- top
이다.
Pop()
void pop()
{
if(q1.empty())
{
while (!q2.empty())
{
int front = q2.front();
q2.pop();
if(q2.empty())
{
break;
}
q1.push(front);
}
}
else
{
while (!q1.empty())
{
int front = q1.front();
q1.pop();
if(q1.empty())
{
break;
}
q2.push(front);
}
}
}
pop은 q1, q2 의 요소를 서로 스위칭 해가며 한쪽이 empty 일때까지 수행한다.
Push()
void push(int d)
{
if(!q1.empty())
{
q1.push(d);
}
else
{
q2.push(d);
}
}
push 함수는 위와 같이 추가해주면 끝이다.
Top()
int Top()
{
int top = -1;
if(q1.empty())
{
while (!q2.empty())
{
top = q2.front();
q2.pop();
q1.push(top);
}
}
else
{
while (!q1.empty())
{
top = q1.front();
q1.pop();
q2.push(top);
}
}
return top;
}
Top 함수는 pop에서 그러했듯이, 스위칭을 수행하지만, 마지막에 요소를 삭제시키지 않고 그대로 반환한다.
tags: Algorithm, Data Structure